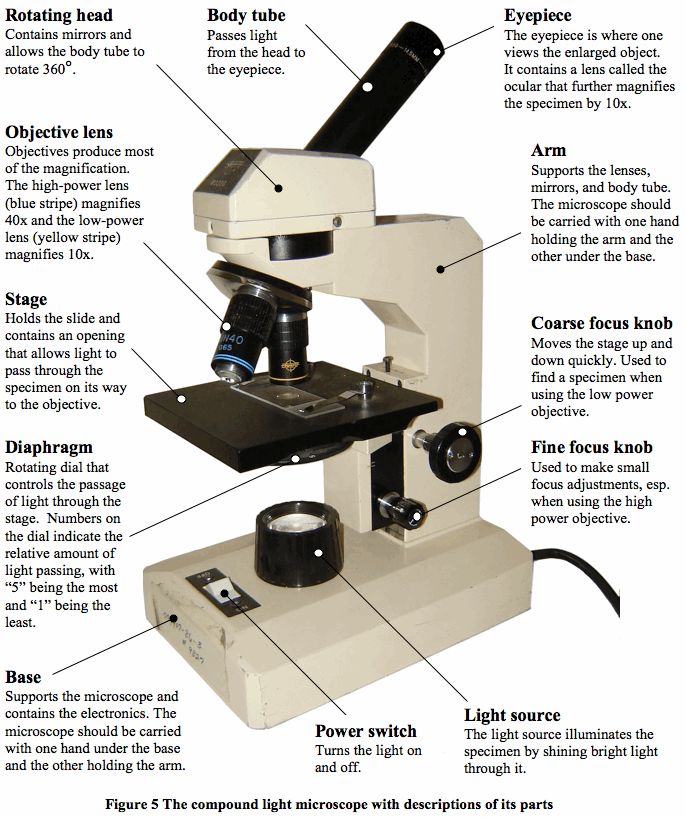
Experiments
|
|
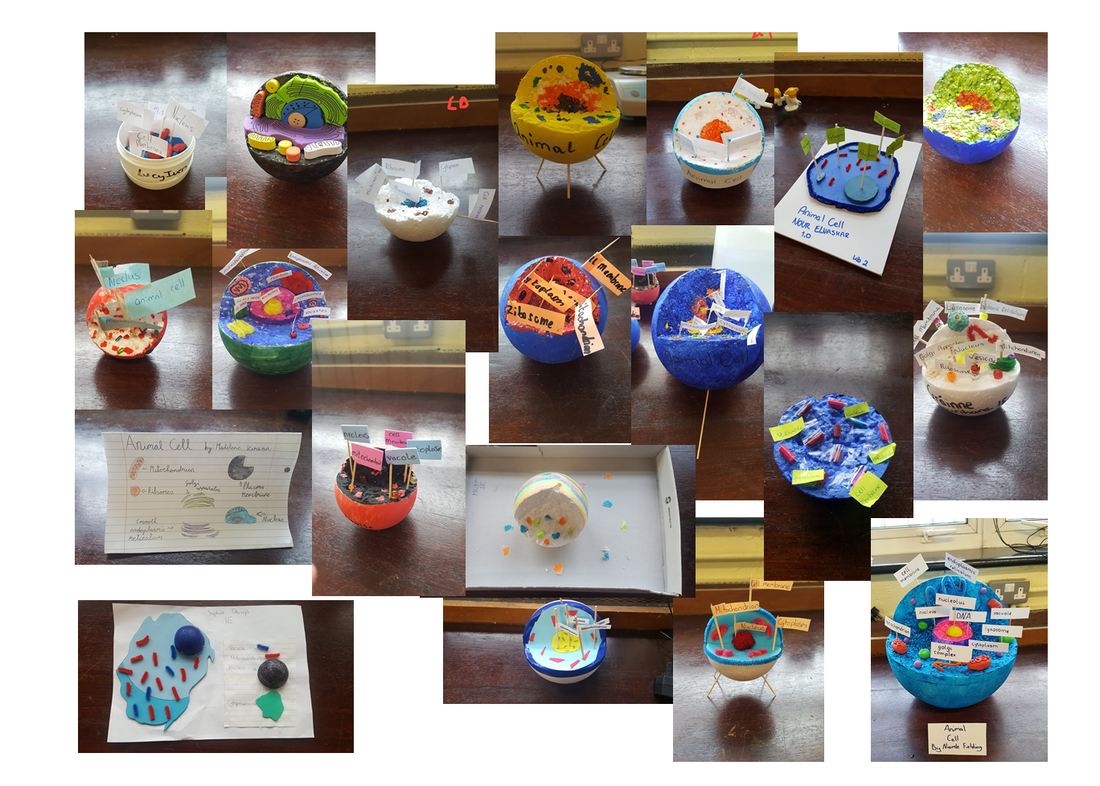
Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common.
Cytoplasm: A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen.
Nucleus: Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell’s activities.
Cell membrane: Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others. It therefore controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Mitochondria: Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.
Ribosomes: A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs.
Cytoplasm: A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen.
Nucleus: Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell’s activities.
Cell membrane: Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others. It therefore controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Mitochondria: Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.
Ribosomes: A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs.
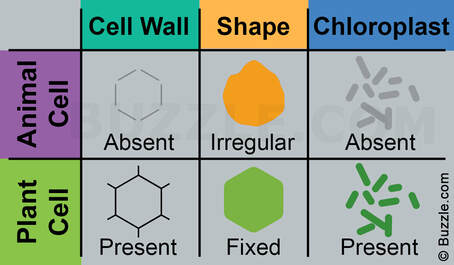
Plant cells also have additional structures:
Chloroplast: Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis.
Cell wall: Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant.
Permanent vacuole: Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid.
Chloroplast: Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis.
Cell wall: Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant.
Permanent vacuole: Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid.
Making a DIY Cell Model: Student Tutorial |
Student Cell Models 2021/22: |
|
|
|