DIY Phases of the Moon project slideshow!
Our Moon doesn't shine, it reflects the sunlight shining on it. There are 8 phases (lunar phases) which repeat every 29.5 days. New Moon, Waxing Crescent, 1st Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, 3rd Quarter & Waning Crescent.
Our Moon doesn't shine, it reflects the sunlight shining on it. There are 8 phases (lunar phases) which repeat every 29.5 days. New Moon, Waxing Crescent, 1st Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, 3rd Quarter & Waning Crescent.
|
|
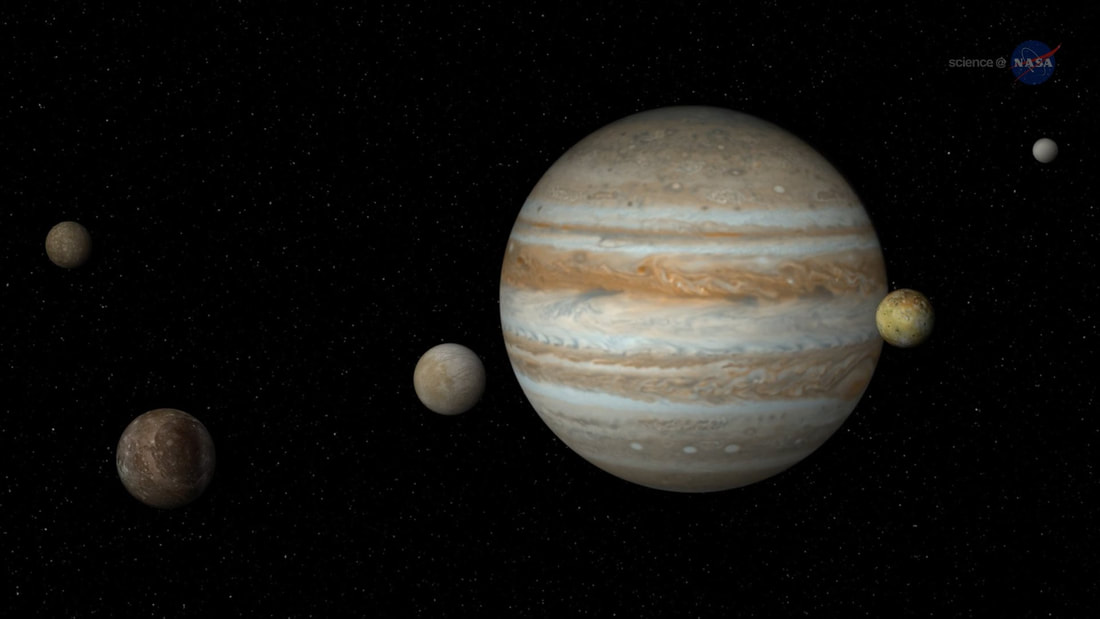
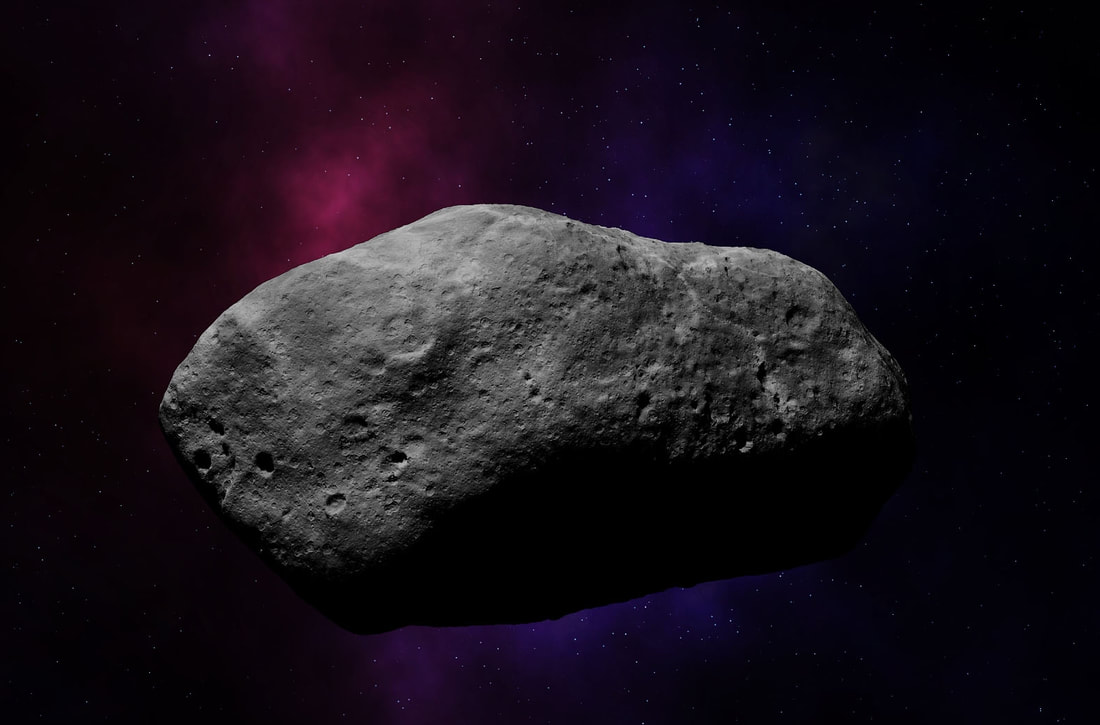
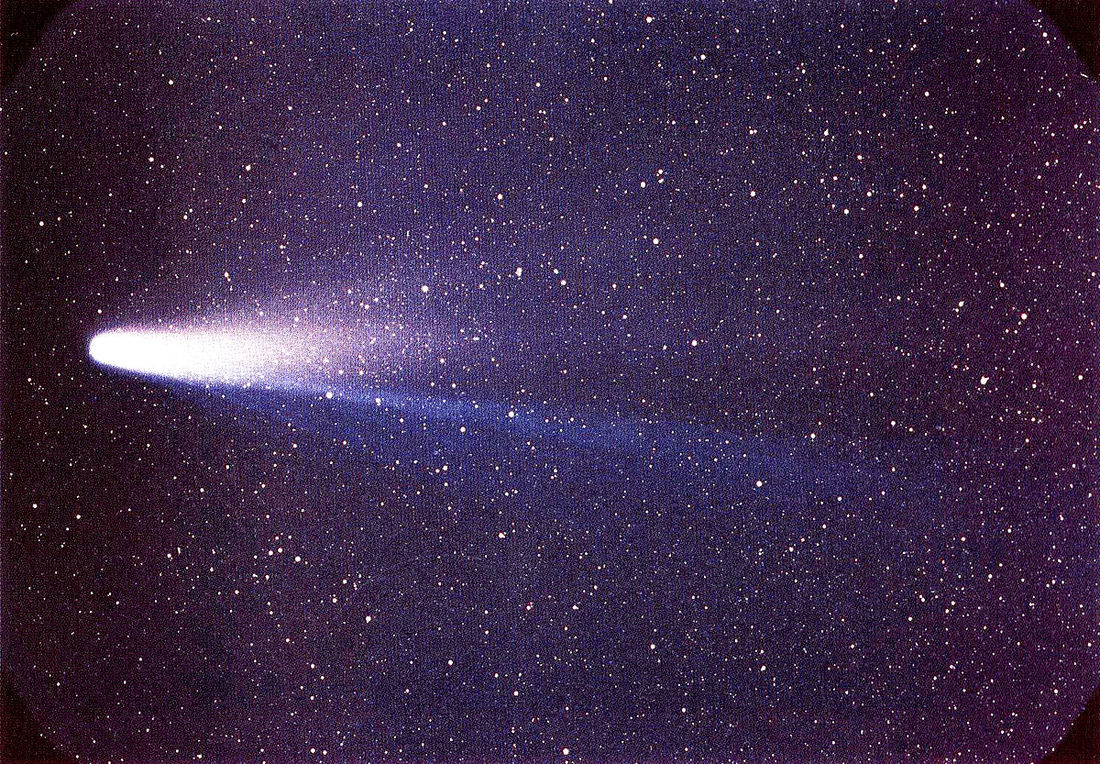
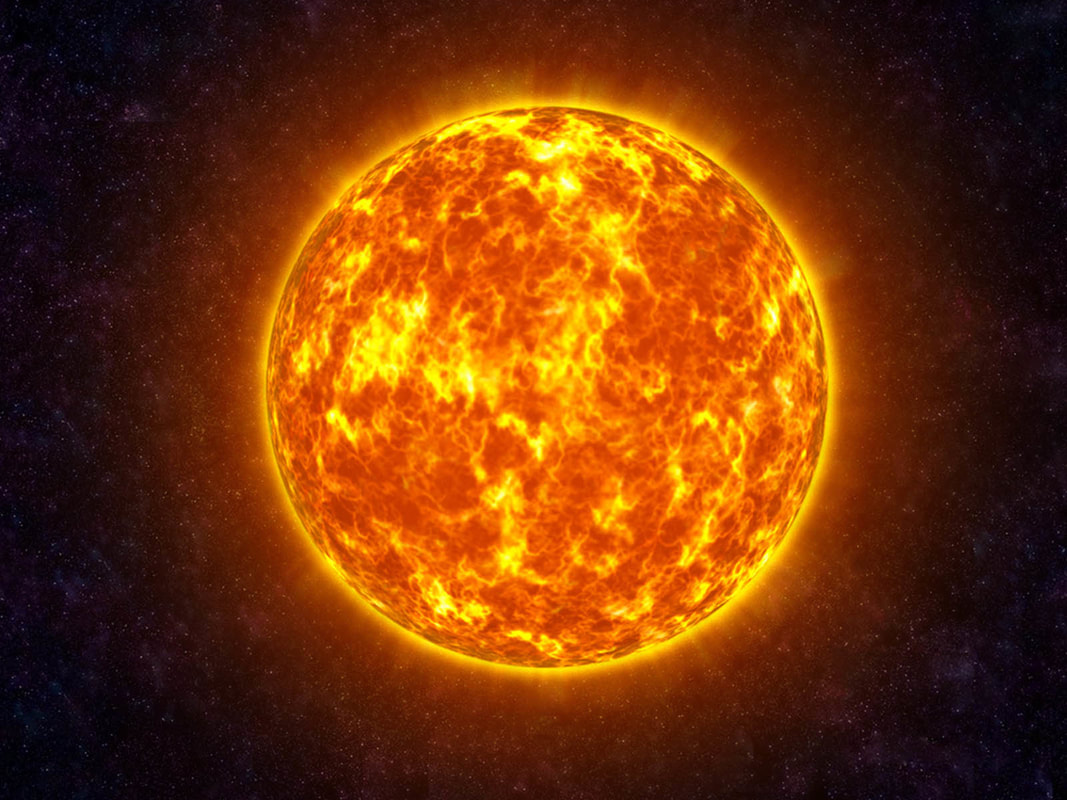
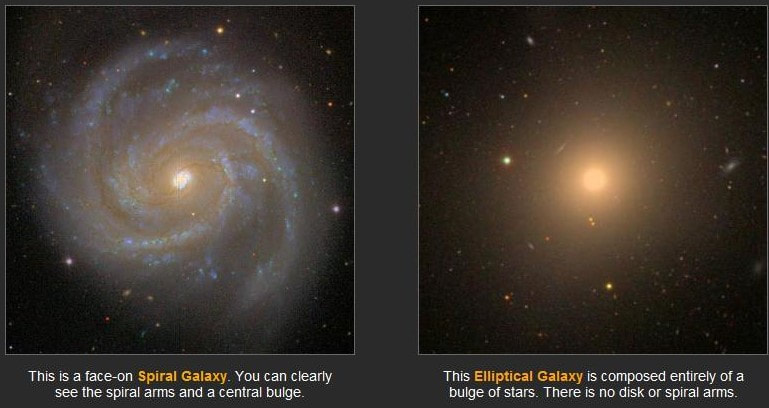
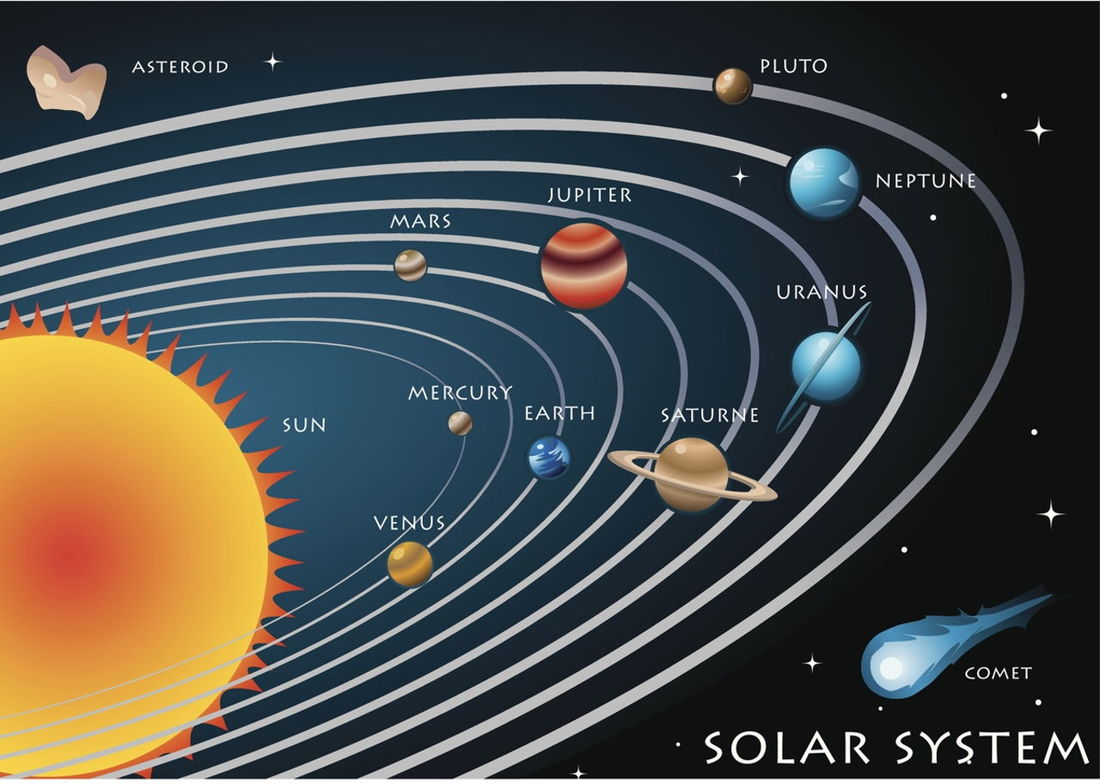
Six TYPES of celestial objects in the Solar system are:
1) Star ( Self luminous ) 2) Planets & Dwarf Planet (Orbits the Sun, rocky or gaseous, atmosphere or no atmosphere, has moons or none) 3) Moon ( Orbits planets, rocky, atmosphere or no atmosphere ) 4) Comet ( Orbits Sun, rocky/icy, atmosphere only when close to Sun, relatively short life span ) 5) Asteroid ( Orbits Sun, rocky, small, no atmosphere ) 6) Miscellaneous ( Space dust, man-made objects e.g. satellites, space probes ) |